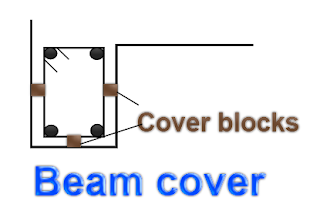
1. Clear cover :
2. Rebar quality:
The steel bar should be straight, having a uniform diameter throughout its length. The bar should look fresh, having a blackish-grey color in its appearance.
The rusted rebar should be avoided as they have low bonding strength with the concrete. The ribs over the bars should be uniform in their thickness & depth, without any breaks in them.
3. Grade of steel:
The grade of the steel bar should be chosen, as mentioned in the reinforcement detail drawings of the beam. You can find the grade of steel embossed over the bar, as shown in the above drawing.
Checking the steel grade is a must, as it shows the yield strength & decides the load-carrying capacity of the rebar.
4. Dia. & spacing of the main bar:
The diameter of the top & bottom main bars of the beam should be checked as per the drawing. The horizontal, as well as vertical spacing between the two bars, should be measured precisely.
5. Dia. & spacing of the stirrups:
6. Corner angle & hook length:
7. Position of the stirrups:
8. Development length(Ld):
9. Bar lapping:
The lap length of the bar should be checked for its proper measurement as given. Care should be taken while providing the lapping of the bar so that, it should fall in the lapping zone of the beam.
Also read: What is lap length in reinforcement bars?/ General rules while providing lap length.
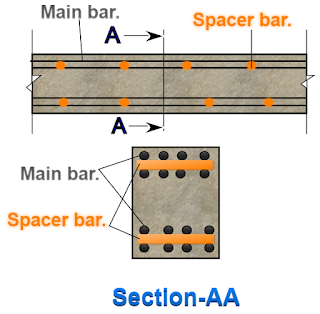
10. Spacer bar:
Also read: What is a spacer bar in a beam?-purpose, spacing & its cutting length.
11. EOS bar:
The diameter, position & length of the extra over support bar should be checked if mentioned in the drawing. Usually, the length of the given EOS bar is at an L/3 distance from the column, where L is the span of the beam.
12. Extra bottom bar:
The diameter, position & length of the extra bottom bar should be checked as mentioned in the drawing. The extra bottom bars are provided at the mid-span of the beam, having 2/3L of the beam span as shown in the drawing.
13. Beam junction:
The lateral ties of the column & stirrup of the beam should be checked for their proper position at the junction of the beam & column. Due to congestion, the bar bender may curtail the main bars or may not place stirrups at the beam end.
14. Binding:
The knot of the tied binding wire should not enter the cover space of the beam. The wire should be pushed inside the stirrup as shown in the drawing.
We have to ensure that all the stirrups are tied firmly so that they won't leave their position at the time of vibration.
👀 To go through all types of construction-related procedures & checklists, click here.
Thank you for going through this article❤. Have a good day 😄.




















No comments:
Post a Comment