Let us now calculate the slope, run & rise in the 3 different drawings as shown below.
1. Slope calculation :
Given data :
Run = 15m.
Rise = 0.5m.
Slope = [run ÷ rise]
= [15m. ÷ 0.5m].
= 30
So, we should provide a gradient or slope of 1: 30
2. Run calculation:
Given data :
Slope = 1: 100
Rise = 0.5m
Run
= [slope x rise]
= [100 x 0.5]
= 50 m.
So, we have to provide a 50m run for every 0.5m rise.
3. Rise calculation:
Given data :
Slope or gradient = 1:30
Run = 12m.
Rise
= [run ÷ slope]
= [12m. ÷ 30]
= 0.4m. or 400mm.
So, for a 12m run, you have to provide a 0.4m. or 400mm. rise.
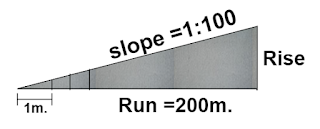
4. Rise per meter calculation:
When we make roads, we cannot provide a rise for the total length as the work should be done in different phases. In such cases, we have to calculate the rise per meter run.
Rise
= [ run ÷ slope]
= [200m. ÷ 100]
= 2m.
Here,
For 200m run, rise = 2m
For 1m. run, rise =?
By cross multiplication,
[1m. × 2m.] = [rise/m. × 200]
Rise/m. = [(1m. × 2m. ) ÷200]
= 0.01m. or 10mm.
If you want to provide a gradient for the 20m. run of the above-given road,
The formula
= [rise/m. × run length]
= [0.01m per m. × 20m.]
= 0.2m. or 200mm.
To go through the articles on Estimation & calculation in civil engineering, click here.














No comments:
Post a Comment